VMware Aria Operations for Applications (formerly known as Tanzu Observability by Wavefront) is a high-performance streaming analytics platform that supports observability for metrics, counters, histograms, and traces/spans. The product is unique because it scales to very high data ingestion rates and query loads. You can collect data from many services and sources across your entire application stack, and can look at details for earlier data that were ingested earlier.
Intro Videos
The first video is a 90 second overview of how you can use explore data and create alerts. Note that this video was created in 2020 and some of the information in it might have changed. It also uses the 2020 version of the UI.
is a 90 second overview of how you can use explore data and create alerts. Note that this video was created in 2020 and some of the information in it might have changed. It also uses the 2020 version of the UI.
In the second conceptual video, the product co-founder Clement Pang explains:
- How to set up the data ingestion pipeline
- How dashboards, charts, and alerts allow you to monitor your environment
- How our histogram and tracing features can give you the full picture of what’s going on.
Note that this video was created in 2019 and some of the information in it might have changed.
What Can I Do?
After you send your data in, you can view it in custom dashboards, alert on problem values, and perform anomaly detection and forecasting.
Charts and Dashboards
Visualize the information in dashboards and charts.
|
 |
Alerts
| To detect problems, you can create alerts directly from charts and specify.
For example, assume in your environment you need to know:
|
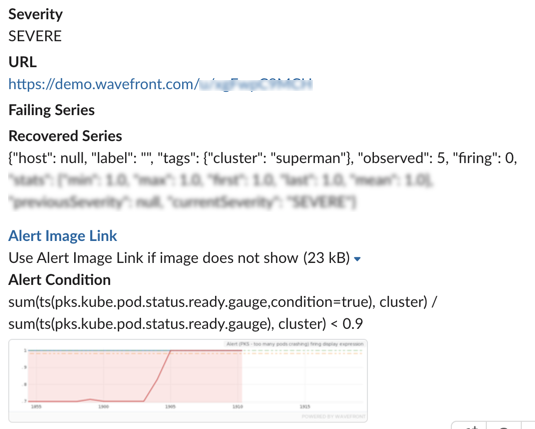 |
Queries
| The Wavefront query language (WQL) allows you to extract exactly the information you need. With filters and functions you can customize your charts so the signal becomes visible in the noise. Initially, many users like the ease-of-use of Chart Builder (shown on the right). Advanced users work with Query Editor. |
 |
Distributed Tracing
| Use Distributed Tracing to work with a service map, examine traces and spans, and drill down into problem areas. |  |
How Do You Integrate With…?
We support over 200 integrations including cloud providers, DevOps tools, big data, and more.
To interact with our service, you can use our rich Graphical User Interface, which includes many pre-built system dashboards, charts, and alerts. You can also use SDKs available on our GitHub page, the Operations for Applications REST API, and CLIs.
In addition, tight integrations with Spring Boot, Kubernetes, and Tanzu Mission Control are available.
Spring Boot
| Wavefront for Spring Boot allows you to quickly configure your environment, so Spring Boot components send metrics, histograms, and traces/spans to the service. After you’ve completed setup, you can examine the data in preconfigured or custom-built dashboards and charts. |  |
Kubernetes
| Use our easy to set up integration to collect real-time metrics from all layers of a Kubernetes environment (clusters, nodes, pods, containers and the Kubernetes control plane). You can visualize the metrics in a rich set of predefined dashboards.
Note that this video was created in 2020 and some the information in it might have changed. |
Tanzu Mission Control
VMware Tanzu Mission Control is a centralized management platform for consistently operating and securing your Kubernetes infrastructure and modern applications across multiple teams and clouds. You can use Tanzu Mission Control to manage your entire Kubernetes environment, regardless of where your clusters reside.
It’s easy to monitor any of the clusters:
Step 1: A user with Administrator privileges enables the integration from Tanzu Mission Control. Step 2: Administrators for individual kubernetes clusters add the integration and start exploring the metrics in predefined dashboards.
How Do I Set Up a Data Ingestion Pipeline?
You can use VMware Aria Operations for Applications with time-series (metric) data, and also with traces and spans, and with histograms from diverse sources.
- Cloud: Perform minimal setup to let the service access the data in your cloud environment. The result is direct ingestion of cloud services data such as Amazon Web Services or Google Cloud Platform.
- Integrations: For other data sources, we support over 200 integrations. You modify a simple configuration file and you’re good to go.
- Start Where You Are: If your environment already has a metrics infrastructure, you can do some pre-processing on the data so that it corresponds to our data format, and send them directly to the Wavefront proxy.
- Direct Ingestion: For some use cases, direct ingestion is the best approach. Consider the proxy benefits before you select direct ingestion.
- Histograms: For high-velocity metrics, Wavefront histograms might be the best solution.
- App Monitoring with Distributed Tracing: For traces, we support Jaeger and Zipkin or any applications that are instrumented with the OpenTracing library. You can also send custom traces using one of our SDKs. Our Application Map GUI supports easy exploration of trace data, RED metrics, etc.
Video: Getting Data In
Note that this video was created in 2018 and some the information in it might have changed.
What Are the Supported Interfaces?
Different users interact with the product in different ways:
- Most users access the graphical user interface (GUI) from a browser. You log in to your instance from a standard web browser, in many cases using an SSO solution. The UI supports different time windows – even an entire year.
- The Chart Builder and the Query Editor allow you to fine-tune your charts and alerts. Access function documentation from the UI or start with the Query Language Reference and click any function on that page for details and examples.
- The REST API allows you to perform UI actions programmatically. The API is based on Swagger, so you can generate the client of your choice.
- For Distributed Tracing, we make a large sets of SDKs available in GitHub.
What’s the Architecture?
Our service runs the metrics collection engine. The service runs in the cloud and accepts data from the Wavefront proxy or through direct ingestion.
- With cloud services, our service pulls the data from your cloud provider (after minimal setup). We support all major cloud providers.
- For on-prem telemetry you have several options:
- Set up a collector agent such as Telegraf, which collects data from your host or infrastructure and sends this data to the proxy.
- Send data from your application code to the proxy by using a metrics library. This works well both for metrics and for traces and spans.
- If you have a custom application, you can send your metrics to the proxy or directly to the service, as long as the data is in one of the supported data formats. For example, if your environment already includes a metrics collection infrastructure, you can do some pre-processing on the data and send them to the proxy.
- The proxy can also ingest metrics from your log files. See Log Data Metrics Integration
