Event sets returned from events() queries support several types of operators and functions. You can combine, compare, and filter events sets. You can generate synthetic events sets, convert events sets to time series, and isolate or create individual events.
Event Set Combination Operators
You can combine two event sets using union, intersect, and the minus (-) operator.
Union
The union operator returns all events that exist in either of the event sets. In its simplest form, this expression
events(type=maintenanceWindow) union events(name="test")
is equivalent to
events(type=maintenanceWindow or name="test")
Intersect
The intersect operator returns all events that exist in both of the event sets. This expression
events(type=maintenanceWindow) intersect events(name="test")
is equivalent to
events(type=maintenanceWindow and name="test")
Minus
The minus (-) operator returns the difference between two event sets. For example, events() - closed(events)) returns all ongoing events.
Event Set Comparison Operators
You can use Allen’s interval algebra operators to compare two event sets.
events(severity=severe) d since(1d)returns all events with severityseverethat occurred in the last day.events(severity=severe) - (events(severity=severe) d since(1d))returns all events with severityseverethat are older than one day.
Event Set Filtering Functions
You can use many of the event functions to filter events. For example, you can return all ongoing events or all closed events.
closed(<events>)- filters out all ongoing and future events, and returns only events that have ended and instantaneous events that occurred the past.
Synthetic Event Set Functions
Some events() functions return synthetic events. These events are displayed by the query, but not stored in Wavefront.
-
since(<events>)- Returns a synthetic event with the same start time as the input event and no end time (converts all events to ongoing).
-
until(<events>)- Returns a synthetic event that starts at the beginning of Epoch time (Jan 1, 1970) and ends where the input event starts.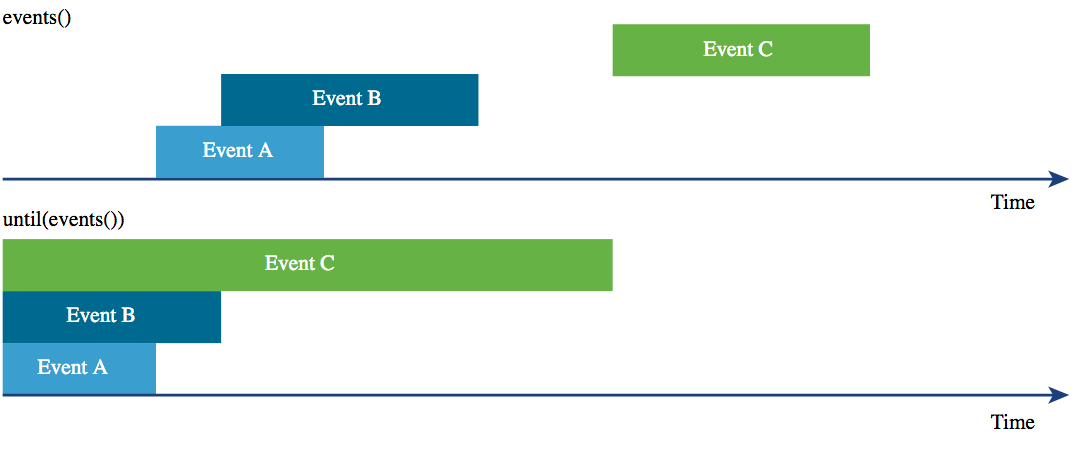
-
after(<events>)- Returns a synthetic ongoing event that starts the moment the input event ends.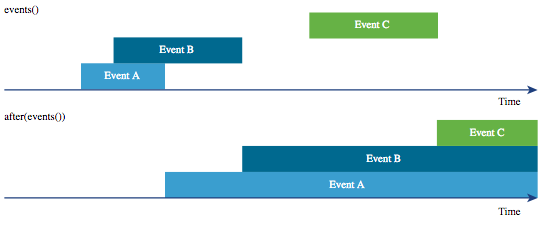
Event Set to Time Series Conversion Functions
Some functions convert event sets to time series.
-
count(<events>)- Aggregates a set of events and converts the result to a single time series, where every data point represents the number of events that started at that time minus the number of events that ended at that time. Instantaneous events are represented as a single “0” value: 1 started minus 1 ended (instantaneous events are defined as events having their end time equal to their start time).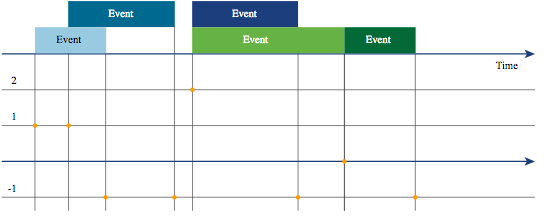
-
ongoing(<events>)- Returns a continuous time series (values reported every second), representing the number of ongoing events at any given moment.
Single Event Functions
Some functions return a single event as opposed to a set of events. These functions either create a single synthetic event or isolate a single event from a series. All functions and operations that accept a set of events also accept a single event.
Isolation Functions
These functions isolate a single event from an event set. If multiple events match the condition, the result is non-deterministic, however, each of these functions always returns just one event.
first(<events>)- Returns a single event with the earliest start time.last(<events>)- Returns a single event with the latest start time.firstEnding(<events>)- Returns a single event with the earliest end time.lastEnding(<events>)- Returns a single event with the latest end time.
Creation Functions
-
timespan(startTimestamp, endTimestamp)- creates a single synthetic event with the specified start and end timestamps. A timestamp can be expressed in epoch seconds or using a time expression such as “5 minutes ago”. For example,timespan("5 minutes ago", "2 minutes ago"). -
since(timeWindow)- creates a single synthetic event that startedtimeWindowago and ended now.timeWindowcan be specified in seconds, minutes, hours, days or weeks (e.g. 1s, 1m, 1h, 1d, 1w). If the time unit is not specified, the function uses minutes.